Outline
-
Introduction
- Definition of ectopic pregnancy
- Importance of early detection
-
Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms
- Early signs
- Advanced symptoms
-
Early Symptoms
- Description of early symptoms
- Importance of recognizing these symptoms
-
Advanced Symptoms
- Description of advanced symptoms
- Potential complications
-
Conclusion
- Summary of key points
- Importance of seeking medical help
-
FAQs
- Commonly asked questions
- Brief answers
Introduction
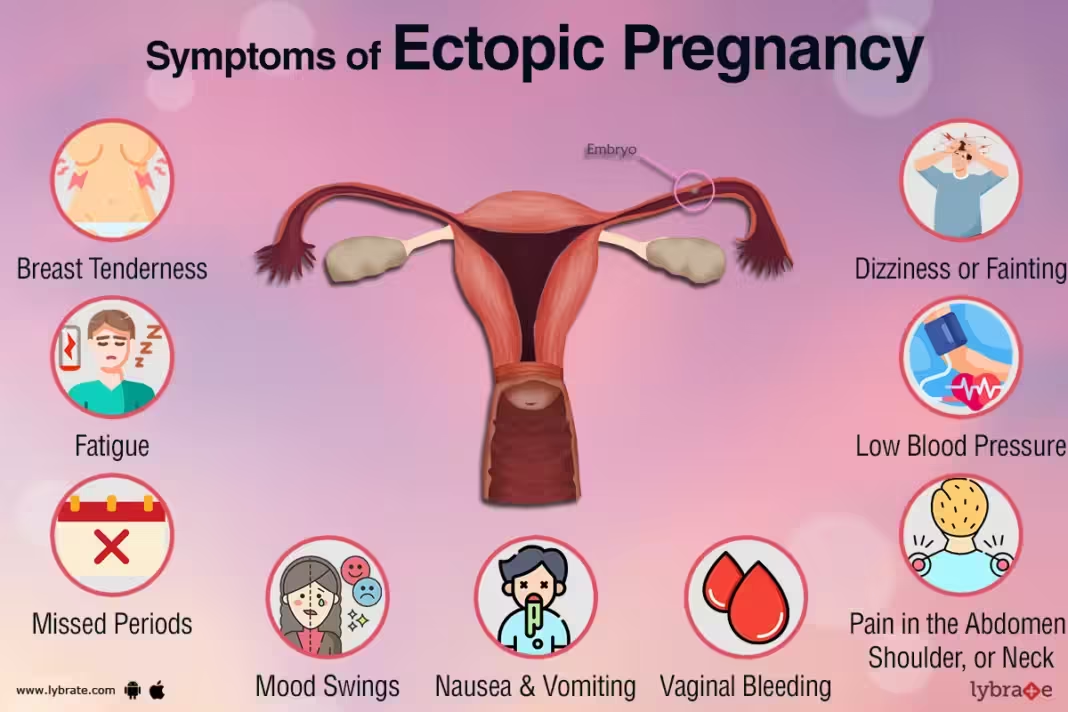
Ectopic pregnancy symptoms occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. Early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy can be subtle and resemble those of a normal pregnancy, including missed periods, breast tenderness, and nausea. However, there are specific signs that can indicate an ectopic pregnancy, such as light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain. These symptoms are often the first indicators and should not be ignored, as early detection is crucial for preventing severe complications.
Advanced Symptoms
As an ectopic pregnancy symptoms progresses, more severe symptoms can develop, signaling potential complications. These include sharp abdominal pain, severe pelvic pain, shoulder pain, and dizziness or fainting. These symptoms are often a result of the fallopian tube stretching and potentially rupturing, leading to internal bleeding. The rupture of a fallopian tube is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention to prevent life-threatening complications. Recognizing these advanced symptoms can be crucial for timely medical intervention and can significantly improve outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition that presents with both early and advanced symptoms. Early ectopic pregnancy symptoms such as light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain can help in the timely diagnosis and treatment of the condition. However, if advanced symptoms such as sharp abdominal pain or dizziness occur, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention to prevent severe complications. Understanding and recognizing these symptoms can save lives and ensure better health outcomes.
FAQs
Q: What causes an ectopic pregnancy? A: Ectopic pregnancies can be caused by conditions that affect the fallopian tubes, such as inflammation, infection, or structural abnormalities. Risk factors include previous ectopic pregnancies, pelvic inflammatory disease, and certain fertility treatments.
Q: How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed? A: Diagnosis typically involves a combination of pelvic exams, ultrasound imaging, and blood tests to measure hormone levels. These tests help determine the location of the pregnancy and assess the condition of the fallopian tubes.
Q: What are the treatment options for an ectopic pregnancy? A: Treatment options include medication to stop the growth of the pregnancy and surgical interventions to remove the ectopic tissue. The choice of treatment depends on the size and location of the ectopic pregnancy and the patient’s overall health.
Q: Can an ectopic pregnancy be prevented? A: While it is not always possible to prevent an ectopic pregnancy, reducing risk factors such as avoiding sexually transmitted infections and addressing any fallopian tube abnormalities can help lower the risk.
Q: What are the long-term effects of an ectopic pregnancy? A: Long-term effects can include damage to the fallopian tubes, which may affect future fertility. However, many women go on to have successful pregnancies after an ectopic pregnancy with appropriate medical care and monitoring.